This section provides a basic guide to designing and building a Meta unit on ARK. The focus is on creating learner experiences.
We recommend you are familiar with the overview of unit structure before starting this section.
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
This section provides a basic guide to designing and building a Meta unit on ARK. The focus is on creating learner experiences.
We recommend you are familiar with the overview of unit structure before starting this section.
When we introduced unit structure we presented the hierarchy of content in ARK as:
The smallest unit in the hierarchy is either a resource or an activity.
A resource is a piece of static, ungraded content designed to present information to the student.
An activity is an item that the student interacts with, either individually or with other students. Some activities can be graded and may contribute to the gradebook.
Teachers can add activities and resources to their units using the activity chooser. To access the activity chooser, enable editing and click Add an activity or resource at the bottom of a section.
When you first open the Activity Chooser, you will see four tabs: All, Activities, Resources and Recommended.
The Recommended tab contains a shortlist of activities and resources recommended at the University of Divinity.
You can star your favourite or frequently used activities and resources and they will show in the Starred tab.
Click the star icon to favourite an activity or resource.
The activity icons are colour-coded according to their various functions:
See the MoodleDocs page for more information: Activity Chooser (4.1)
This page introduces teaching staff to the text editor in ARK.
When adding content to activities and resources, teachers will be able to write content directly to text areas in ARK using the text editor.
This document describes the interface for the default text editor, Atto. The new version of ARK (Moodle 4.1) introduces an alternate editor, TinyMCE which is more featured and will become the default in future versions. To change the text editor and for help on using TinyMCE, see MoodleDocs: TinyMCE editor.
This document largely provides advice on effective formatting and use of media in ARK and is applicable for both text editors.
The text editor in ARK is a powerful interface, and is similar to working with other text editors such as Microsoft Word. However, this guide contains a few key recommendations to ensure your content is accessible to all users and is consistent with how learners access content across the internet and other University of Divinity resources.
If you’re unfamiliar with the interface, jump to the text editor interface first.
Eye-tracking studies have consistently found that users scan content on the internet.1 This makes the layout and styling of your content, including on ARK, particularly important. Screen reading software uses pre-defined markers to allow vision-impaired users to more easily navigate the page but it requires those entering content to be consistent with those conventions.
The style dropdown, marked (2) on the screenshot below, presents the key styles that a screen reader will use to navigate the page. Heading levels should indicate the rank of the content, with large headings being the most important, and headings of same importance being the same size. Skipping headings can be confusing and should be avoided.2.
The top row of the editor gives easy access to bold and italics. These text effects can be difficult to read if they are used excessively and so should be reserved for emphasis.
The second row of the toolbar gives the ability to add underline, strikethrough, subscript and superscript.
To create a link, select the text and then click the chain icon, marked (9) on the screenshot below. Paste the URL into the field.
To remove a link, select the text with the link and click the break chain icon, marked (10) on the screenshot below.
You can insert or embed images, video and interactive content in text areas using the text editor.
The practice of inserting or embedding images, video and interactive content can have Copyright implications. It is advisable to seek out images and media that are released under licenses that allow for sharing such as the Creative Commons license.
For more information contact your library staff or see the Australian Copyright Council.
Most browsers will allow you to drag and drop an image from your computer to the text editor. Alternatively, you can click the image icon, marked (12) on the screenshot below. To edit the settings of an image already placed in a text area, click the image and then select the image icon.
The image properties dialogue allows you to paste a link to an image elsewhere on the internet. Always place an image description to assist students using a screen reader or to explain the image in the event the link breaks.
Where possible, resize the image before uploading it to ARK to reduce the file size and subsequent load time of your unit. As a guide, images covering the full width of a course area should be no more than 1200 pixels wide. Reduce the size accordingly for images only displaying at part width of the text area (see “Best Image Size for Websites” for more information).
You can change the size and relative position of the image using the image properties box. Select Auto size to avoid warping the image.
As with images, audio and video can be dragged and dropped into the text editor. Links to some video hosting sites such as Vimeo or YouTube will automatically be converted into embedded content (if you don’t want this behaviour, ask your ARKLO for instruction on disabling the Multimedia Filter).
Audio and video should be hosted on a hosting site such as Vimeo to avoid adding server load and slowing ARK for all users.
The insert media dialogue allows instructors to change the size of the content, adjust playback settings and add additional subtitles or captions.
H5P interactive content can be inserted with the H5P icon, marked (17) on the screenshot below. Creating H5P content is a more advanced concept and will be covered elsewhere. More information is available on MoodleDocs: H5P.
The HTML code, marked (16) on the screenshot below, allows instructors with HTML understanding to change the appearance in ways not available in the editor menus.
The text editor is used extensively throughout ARK, including posting in forums, editing section headings, activity descriptions, quiz answers and the content of blocks.
There are two rows to the editor toolbar, which can be expanded using the expand button, marked 1 below:

| (1) Expand | (2) Style | (3) Bold | (4) Italics | (5) Unordered list |
| (6) Ordered list | (7) Decrease indent | (8) Increase indent | (9) Create link | (10) Remove link |
| (11) Insert emoticon | (12) Insert picture | (13) Insert video | (14) Record audio | (15) Record video |
| (16) Manage embedded files | (17) Insert H5P |
| (1) Underline | (2) Strikethrough | (3) Subscript | (4) Superscript | (5) Left align |
| (6) Centre align | (7) Right align | (8) Equation editor | (9) Insert character | (10) Table |
| (11) Clear formatting | (12) Undo | (13) Redo | (14) Accessibility checker | (15) Screenreader helper |
| (16) Edit html code |
Nielsen, Jakob. 1997. “How Users Read on the Web.” Nielsen Norman Group. September 30, 1997. https://www.nngroup.com/articles/how-users-read-on-the-web/. ↩︎
“Headings • Page Structure • WAI Web Accessibility Tutorials.” n.d. Www.w3.org. https://www.w3.org/WAI/tutorials/page-structure/headings/. ↩︎
This document covers the methods and tools available for presenting static information to students on ARK. It will introduce the Text and Media, Page, File and Book Resources and cover basic user interface and pedagogical design strategies to aid navigation for students.
There are multiple ways to present content or information to learners in ARK. The screenshot below shows the most common Resources:
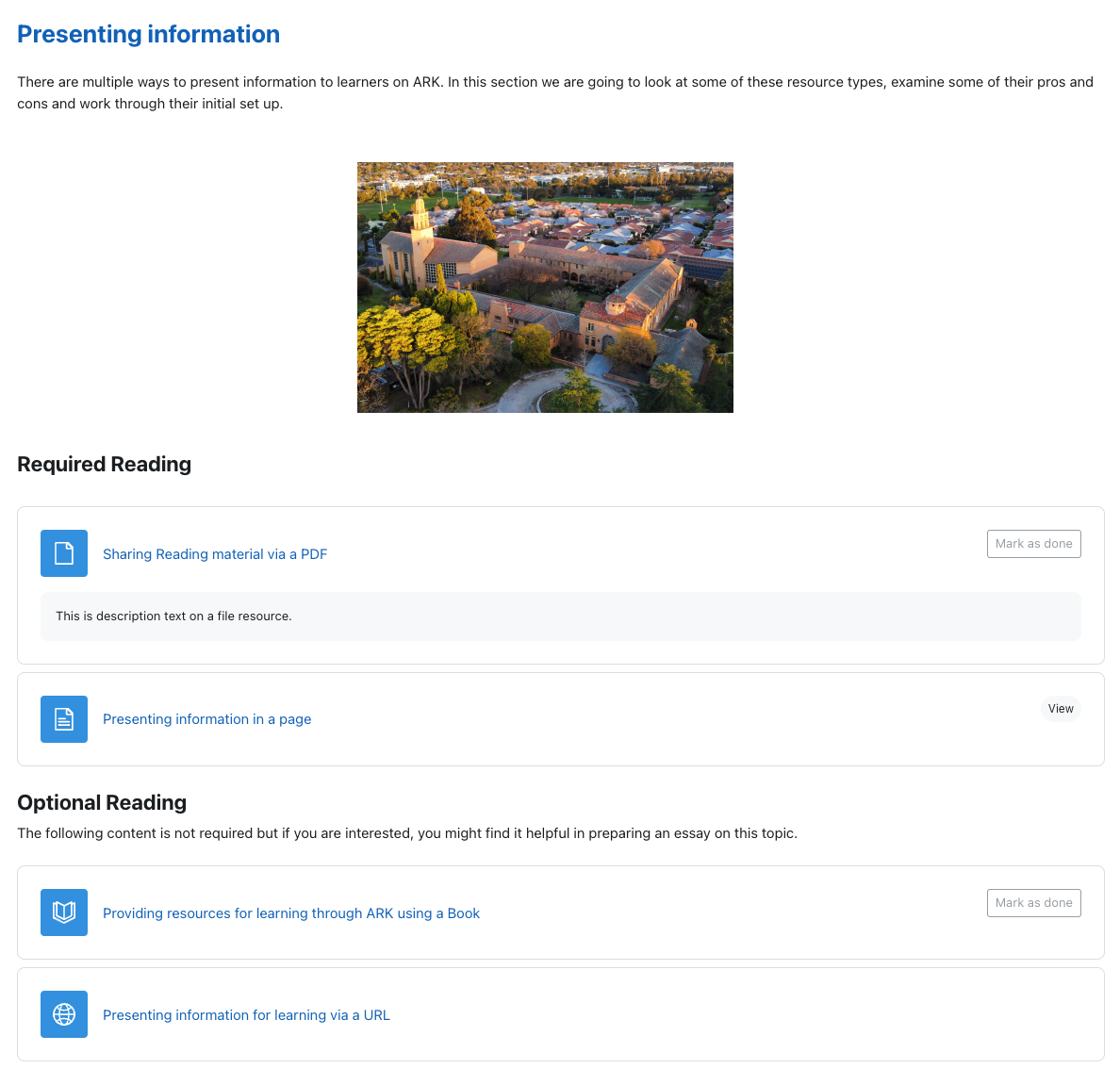
1 1 2 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 Screenshot of a sample section in Moodle. Hover over the numbers for more detail.
The above Resources can be grouped into three types: presentation resources (descriptions and, Text and Media Areas), external resources (URL) and internal resources (Page, Book and File) .
Text and Media Areas (previously called Labels) and Descriptions help students navigate the sections in an ARK unit. They can function as signals – to point students to where information is or how it is arranged – or as direct instruction – to explain a concept or set up an activity.
Descriptions sit below an Activity or Resource and are set in the settings for the Activity or Resource. You can use a Description to provide context for a particular Activity or Resource, or provide a citation.
A Text and Media Area is a way of presenting content on the section page and can be used to group or separate Activities and Resources, provide instruction or deliver content. In the example below, the heading is placed before the first reading to signal to students what the reading is for, a subsequent Text and Media Area sets up an activity, and the video is placed in a Text and Media Area for easy viewing.
In many cases, the learning resources you provide to students will be outside of ARK, which you can link to (such as an external website or Library Hub resource).
A URL Resource allows you to provide a link to a resource external to ARK such as the Library Hub or a website. While it is possible to hyperlink from any text in a Text and Media Area or description, a URL resource is preferred as it allows you you to set completion requirements to track or signal progress to the student.
ARK offers a few Resources and Activities to present content. The simplest of these are Page and Book. Pages and Books both allow you to build web content in ARK with text, images and embedded content. They are considered Resources as the only behaviour available to students is to view the content. Both Pages and Books are easily printed to PDF by students. You can also upload a File (such as a PDF or other downloadable resource)
Other options: other methods of presenting content include the Lesson activity and the H5P activity. These activities are more complicated to setup and will be covered elsewhere.
Page Resources are best used to present content that doesn’t need extensive scaffolding for students to process or to present information that would take up too much space on the section page. For example, a Page might be used to provide an extended bibliography for a topic or to collate instructions for a learning task such as an assessment.
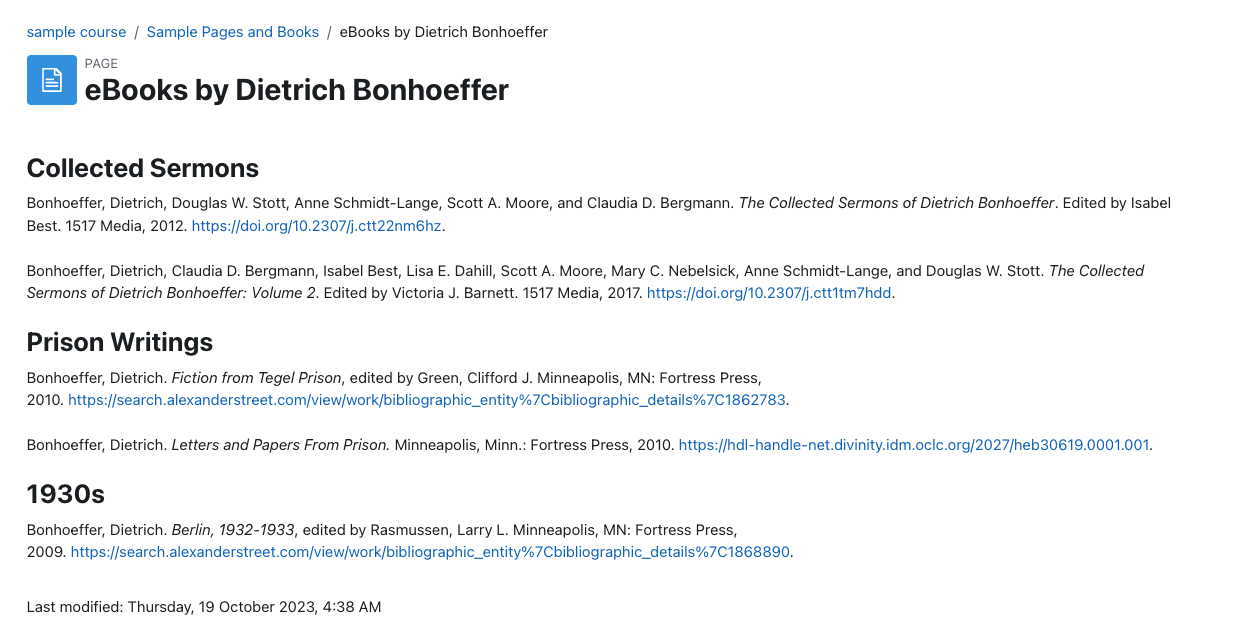
An example of a Page showing a bibliography of selected Library Hub resources.
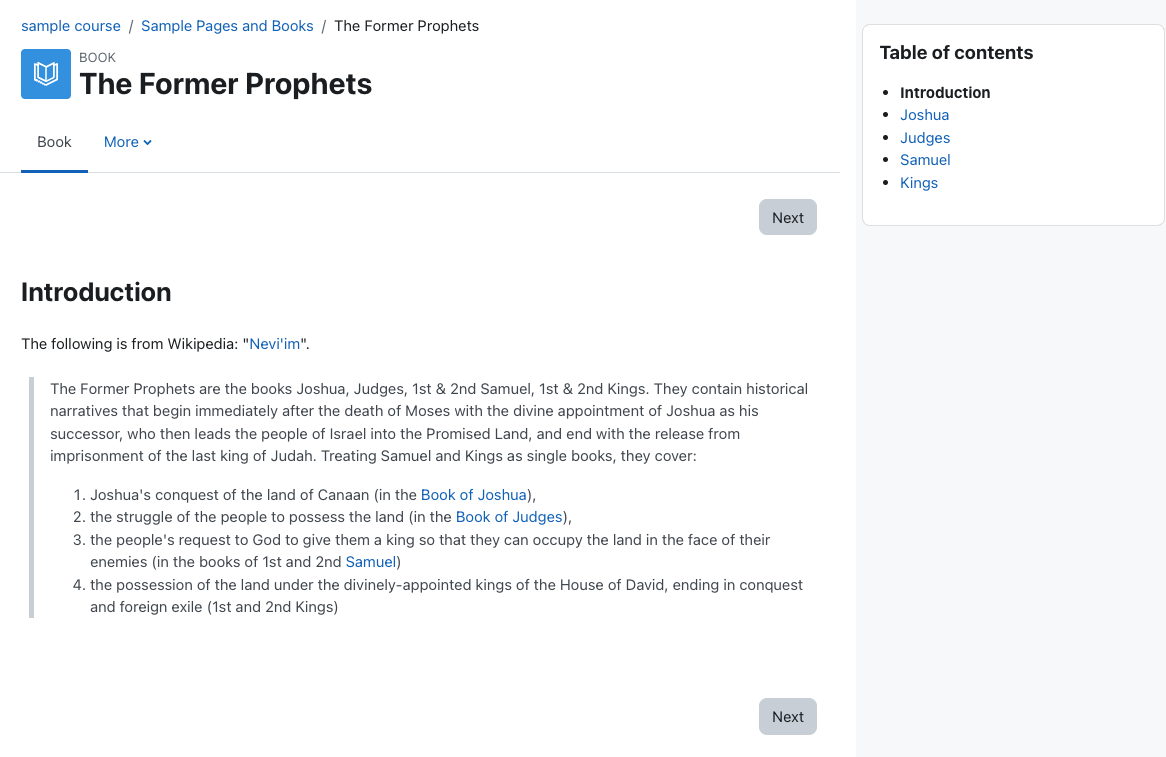
A Book is a set of pages presented in a book-like format. Books are best used to present related ideas that together are too much to contain to a single Page. For example, prior to a lecture on the prophets, you might wish to ensure students have a basic overview of the content and themes of each. You could create a Book with a short introduction to each of them.
A File Resource allows you to share files with students. This is most commonly used to upload PDFs but can also be used to provide PPTs, Word documents or audio recordings.
The practice of uploading files, images and documents can have Copyright implications.
For more information contact your library staff or see the Australian Copyright Council.
This page shows the process for displaying Zoom information in a meta unit on ARK. It requires Editing Teacher permissions and a Zoom account issued by either the University of Divinity or Yarra Theological Union.
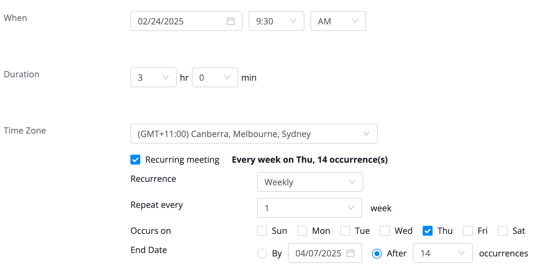
Note: the start date is displaying in MM/DD/YYYY format
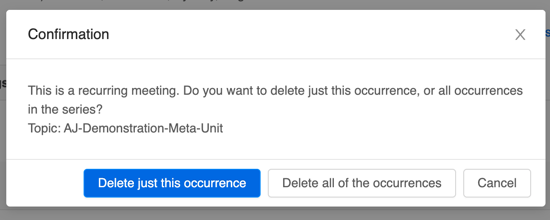
There is no need to create multiple meetings if your class meets on different times or skips some weeks. Once you have scheduled the recurrence, you can delete the instances that you don’t need.
In the screenshot above, the class is scheduled for 14 recurrences. That way, once we’ve Saved our new meeting we can delete the two mid-semester break weeks: